Influenza, more commonly known as flu, is a highly contagious, acute viral infection of the respiratory tract. The typical incubation period is 1-3 days but this can vary.
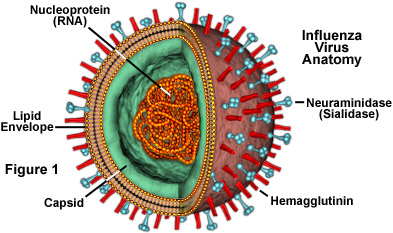
Image Source:
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology: The Influenza (Flu) Virus
Types of Flu Virus
There are 3 types of flu viruses that affect humans:
Type A – usually the more serious type, responsible for yearly outbreaks and pandemics.
Type B – tend to cause less severe disease and smaller outbreaks affecting mostly children.
Type C – causes mild illness similar to the common cold.
A fourth type of virus, known as D virus, exists but this primarily affects cattle and is not known to infect or cause illness in humans.
Influenza viruses are categorised by the antigens on their surface. These are one of two types:
- Haemagluttinin (H), this antigen binds to the cells they are infecting, there are 18 different subtypes.
- Neuraminidase (N), this antigen allows the virsues to be released from an infected cell after replication, there are 11 different subtypes.
We see these put together to describe strains e.g. H1N1 (swine flu), H5N1 (bird flu) and H3N2 (Hong Kong flu).
