Chickenpox Complications
The website NICE Chickenpox has useful information on Chickenpox complications.
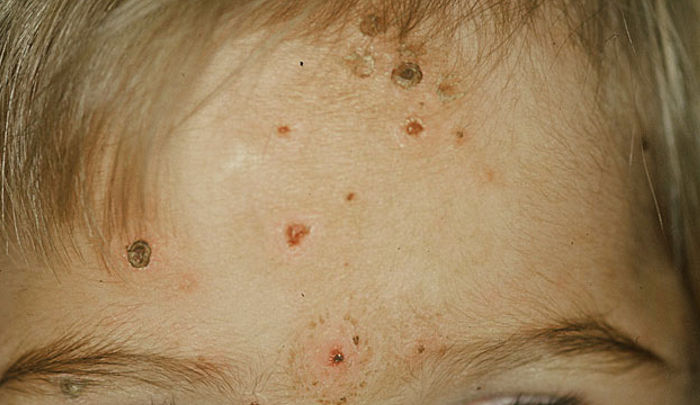
There are a wide range of complications associated with chickenpox; these are more common in high-risk groups such as pregnant women, newborns and those who are immunocompromised. In rare circumstances, some of these complications may be fatal.
Some of the more common complications could be:
Secondary bacterial skin infection
- The most common complication associated with chickenpox is secondary bacterial infection of the skin, most often caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes.
- This can accentuate any scarring of the skin that may occur after chickenpox, but infections can be minimised through use of antibacterial soaps and by discouraging scratching.
Pneumonia
- Pneumonia as a complication of chickenpox is rare in healthy children but occurs with increased frequency in immunocompromised people of all ages and in immunocompetent adolescents and adults.
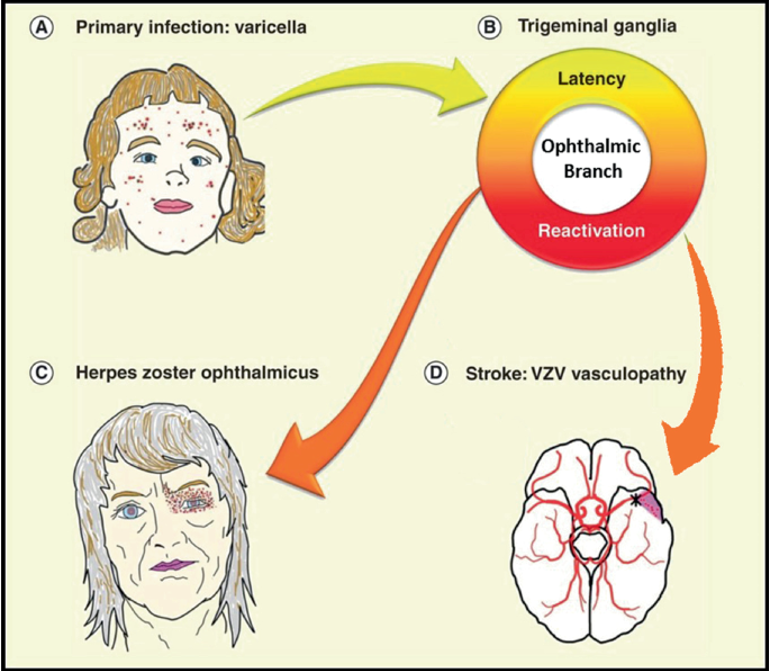
Neurological Complications
- If VZV travels to the central nervous system (CNS), a range of neurological complications can occur; most common of these are encephalitis and cerebellar ataxia.
- The incidence of this kind of complication is rare; it is estimated to be 1-3 per 10,000 cases.
- Neurological symptoms generally occur around one week after rash onset.