Phishing Attacks
A phishing attack is a malicious attempt to collect information such as usernames and passwords. These mostly come in the form of emails but can also be text messages or phone-calls. Phishing attacks are dangerous because unauthorised users can access your data using your own credentials. This could lead to identity theft, financial loss or reputation damage. They can also be a way to install malware on devices.
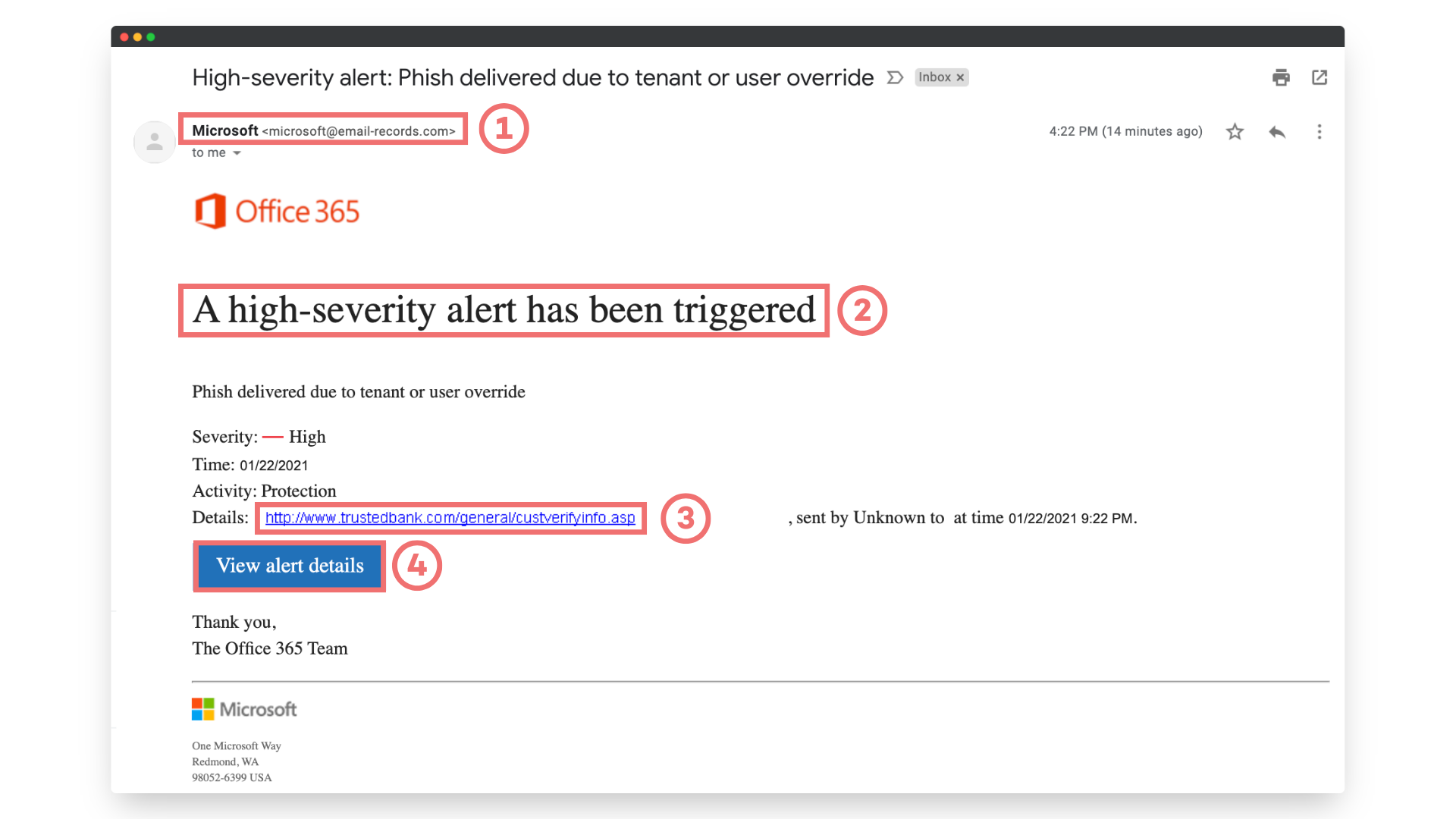
Spotting phishing attacks can be quite difficult as they are constantly evolving to be more complex. This module focuses on emails as they are the most common form of phishing attack, but you can apply these principles to other forms of communication.
Here are some common things to look for to check if an email is genuine or not:
Check the sender information
- Is it from someone you have an account with and would expect to be contacted by?
- Is the name of the sender spelt correctly?
- Look for abbreviations and change of style of lettering e.g. Numark v Numɑrk (the a is a different format) v Nurnark (an r and n have been used instead of an m)
- Does the sender's address differ from the organisation's usual email format? E.g. training@numark-central.co.uk v training@nm.co.uk (the domain has been shortened)
If you are looking at an email and the answer to any of these questions is “yes”:
- Don’t click any links or download any attachments and report the email. Most email providers have a function for this.
If you are not sure if an email is fraudulent contact the sender using an alternative means of contact e.g. phone number and ask them if it is legitimate.