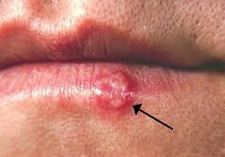
Genital herpes is contagious and is caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) which is passed on by direct contact. The virus attacks any moist lining of the body and can affect parts of the body such as the mouth, eyes and genital areas. When the virus affects the mouth it causes cold sores.
The condition is chronic (long-lasting) and a patient often experiences recurrences. In the first two years of infection a patient may see a recurrence rate of four to five times but over time the frequency decreases. The condition can lay dormant and many people are unaware that they are a carrier.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes
When first infected the patient does not always present with symptoms and it may take a few months or even years for the symptoms to appear. If symptoms appear when first infected they are usually more severe than any future recurrences, this is known as primary infection.
Primary infection can cause the following symptoms:
- Red blisters around the genitals, rectum, thighs and buttocks which can burst and leave open sores
- In women, blisters and ulcers can appear on the cervix or lower womb
- Pain when urinating
- Increase in vaginal discharge
- A high temperature of 38°C (100ºF) or over
- General feeling of being unwell
The symptoms may last for up to 20 days. Any blisters will scab over and heal without leaving any scarring.
A dormant infection can be reactivated at any point and a sign that the symptoms may have been triggered is a tingling, burning, or itching sensation around the genitals and sometimes down the leg which will occur before the blisters appear. The primary symptoms may or may not all occur during a recurrence, any symptoms will usually last for up to 10 days.
HSV can lie dormant and it is not fully known why recurrences happen but it is thought that the following trigger factors may be responsible:-
- Friction in the genital area during intercourse
- Stress
- Being unwell
- Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
- Exposure to ultraviolet light e.g sunbeds
- Having a weakened immune system e.g. after being treated for cancer
- Surgery on the genital area
Treatment for Genital Herpes
There is no cure for genital herpes, but the symptoms can be managed and it is important to advise patients that should use condoms to reduce the risk of passing it on to their sexual partner.
