Travel Related Diseases Preventable with Vaccines

There are some very serious diseases found in other parts of the world that people in the UK won’t be protected against; therefore, it’s important that patients do their research.
Travellers should seek advice from a pharmacist or GP 8 weeks before they are due to travel, as some vaccines may need to be administered in advance, so that the body can develop immunity. Other vaccines may need to be given in scheduled doses over a given length of time.
Some countries may require that people are protected from certain diseases and prove this (with a certificate) before they are allowed to enter.
Some of the most common travel vaccinations are:
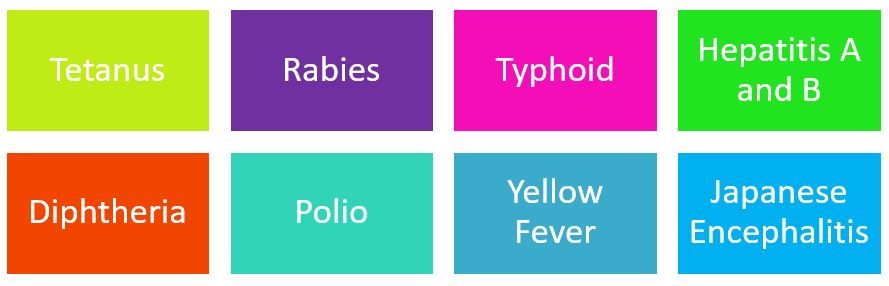
The traveller should find out from their GP whether their UK vaccinations are up to date. Not all travel vaccinations are routine vaccinations and available free on the NHS. Even when vaccines are recommended for a certain country there may be a payment involved for the customer. The payment does not just cover the vaccination cost but also the cost of administering the vaccine and necessary paperwork involved.
If your pharmacy provides a travel vaccination service, ensure your customers are aware – use this opportunity to engage your customers with the service.
To read more on travel vaccinations customers can be signposted to the NHS Travel Vaccinations website.
Below you will find a list of vaccine preventable common travel related diseases that you can recommend to your traveller including information on each disease and prevention tips. Clicking the name directs you to the NaTHNaC website for that disease
Chikungunya
What is it? An unpleasant viral infection caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). It's spread through mosquito bites.
Prevention: Travellers can reduce their risk of being ill from chikungunya by following advice to prevent mosquito bites and getting vaccinated before they travel.

Cholera
What is it? A potentially fatal bacterial disease caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with Vibrio cholerae.
Prevention: Travellers can reduce their risk of being ill from cholera by ensuring good personal hygiene and following advice on preventing food and water spreading disease.
Diphtheria
What is it? Diphtheria is a highly infectious bacterial infection that can affect the nose and throat (respiratory diphtheria), and sometimes the skin (cutaneous diphtheria).
Prevention: Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent infection. Travellers should ensure they are up to date with their routine vaccines according to the NHS immunisation programme.
What is it? Tetanus is a vaccine-preventable disease caused by a toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium tetani. Tetanus spores are found in soil throughout the world.
Prevention: Travellers should have completed (or be up to date with) a primary UK vaccine course according to the NHS vaccination schedule. If visiting countries where medical facilities may be limited, a booster dose of a tetanus-containing vaccine is recommended if the last dose was more than ten years ago.
What is it? Poliomyelitis (polio) is a potentially paralysing, vaccine preventable, viral infection. The virus is transmitted through food or water contaminated by infected human faeces or by direct contact with an infectious person.
Prevention: An effective vaccination against polio is available. In addition to vaccination travellers should ensure good personal hygiene and follow advice on prevention of food and water-borne diseases.
What is it? Hepatitis A is a highly infectious virus that can cause inflammation of the liver.
Prevention: The virus is usually transmitted through food or water contaminated by human faeces or by direct contact with an infectious person. The risk of acquiring hepatitis A can be reduced by ensuring good personal hygiene and following advice on the prevention of food and water-borne diseases.
What is it? Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver spread by direct contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person.
Prevention: All travellers should avoid contact with blood and bodily fluids.
Typhoid
What is it? Typhoid and paratyphoid (also known as enteric fevers) are infections acquired by the ingestion of food or water contaminated by Salmonella Typhi and Salmonella Paratyphi A, B or C.
Prevention: The risk of acquiring Typhoid can be reduced by vigorous food and water hygiene precautions.
What is it? Japanese encephalitis (JE) is a viral infection of the brain transmitted to humans by mosquitoes in parts of Asia and the Pacific Rim.
Prevention: The risk of acquiring JE can be reduced by insect bite avoidance, particularly between the hours of dusk and dawn, when Culex mosquitoes are most active.
What is it? Measles is a highly infectious viral illness with the potential for serious and life-threatening complications.
Prevention: Individuals who have never had measles or are unvaccinated maybe at risk when visiting countries with reported cases, especially when visiting friends or relatives. All UK travellers should ensure they are vaccinated with the MMR.

Meningococcal
What is it? Meningococcal disease is a rare, but potentially devastating infection. It is caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis of which there are 6 disease-causing strains called serogroups (A, B, C, W, Y and X).
Prevention: Individuals should seek advice about their risk of meningitis prior to travel. Meningococcal disease in travellers is primarily a risk for those visiting areas prone to outbreaks or an area where a known outbreak is occurring.
What is it? Rabies is a viral disease transmitted to humans usually by a bite or scratch from an infected animal (usually a dog). The virus attacks the central nervous system causing, progressive damage to the brain and spinal cord. Once symptoms are present, rabies is almost always fatal. Rabies is also covered later in this module.
Prevention: Contact with wild or domestic animals during travel should be avoided.
What is it? Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infection usually transmitted through the bite of an infected tick.
Prevention: Avoid known tick-infested areas of forest and woodland. Practice bite avoidance methods. Check the body for ticks regularly. Remove ticks as soon as possible.
What is it? Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection most commonly spread from person to person through the air by coughing and sneezing.
Prevention: Travellers should avoid close contact with individuals known to have infectious pulmonary TB.
What is it? Yellow fever (YF) is a vaccine preventable viral infection transmitted predominantly by certain species of day biting mosquitoes. YF virus can cause an illness that results in jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) and bleeding, with severe damage to the major organs. The death rate is high in those who develop severe disease.
Prevention: Those visiting YF risk areas should practise meticulous mosquito bite avoidance. A highly effective live YF vaccine is available and in general vaccination is recommended for all persons visiting countries where there is a risk of YF virus transmission. Some countries will not let a person into their country unless proof of vaccination can be shown so customers need to be aware of this. The Fit For Travel NHS Yellow Fever webite has useful information on this to allow you to support your customers. Also, the NaTHNaC Yellow Fever Zone website gives useful information for health professionals and staff (including the community pharmacy) managing a yellow fever vaccination centre (YFVC). More information on setting up a YVFC is found later in this module.

Dengue
What is it? Dengue is an infection caused by the dengue virus of which there are four different types (serogroups). The disease is transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. A vaccine was licenced in the UK in 2023.
Prevention: Mosquito bite avoidance is recommended as dengue is spread by day-biting mosquitoes.