Before vaccination
Vaccination should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations in the UK Health Security Agency Green Book. You should:
- Select the correct product and dose for the recipient.
- Check the vaccine is within expiry date.
- Check the colour and composition of the vaccine matches the description in the product’s SPC, which can be found on the electronic Medicines Compendium.
- Ensure you have the correct needle attached, the recommended needle is a 23 gauge (width of needle) and 25mm in length. For IM and SC injections, the needle needs to be sufficiently long to ensure that the vaccine is injected into the muscle or deep into subcutaneous tissue. In larger patients a longer needle may be required, e,g Green 38mm.
- Ensure there are no contraindications to administration.
- The recipient is fully informed about the vaccine and has given relevant consent.
- The recipient is aware of possible adverse reactions due to vaccination, such as pyrexia, sore arm and allergic reactions.
Techniques
In community pharmacy the flu vaccine is generally administered in the deltoid muscle using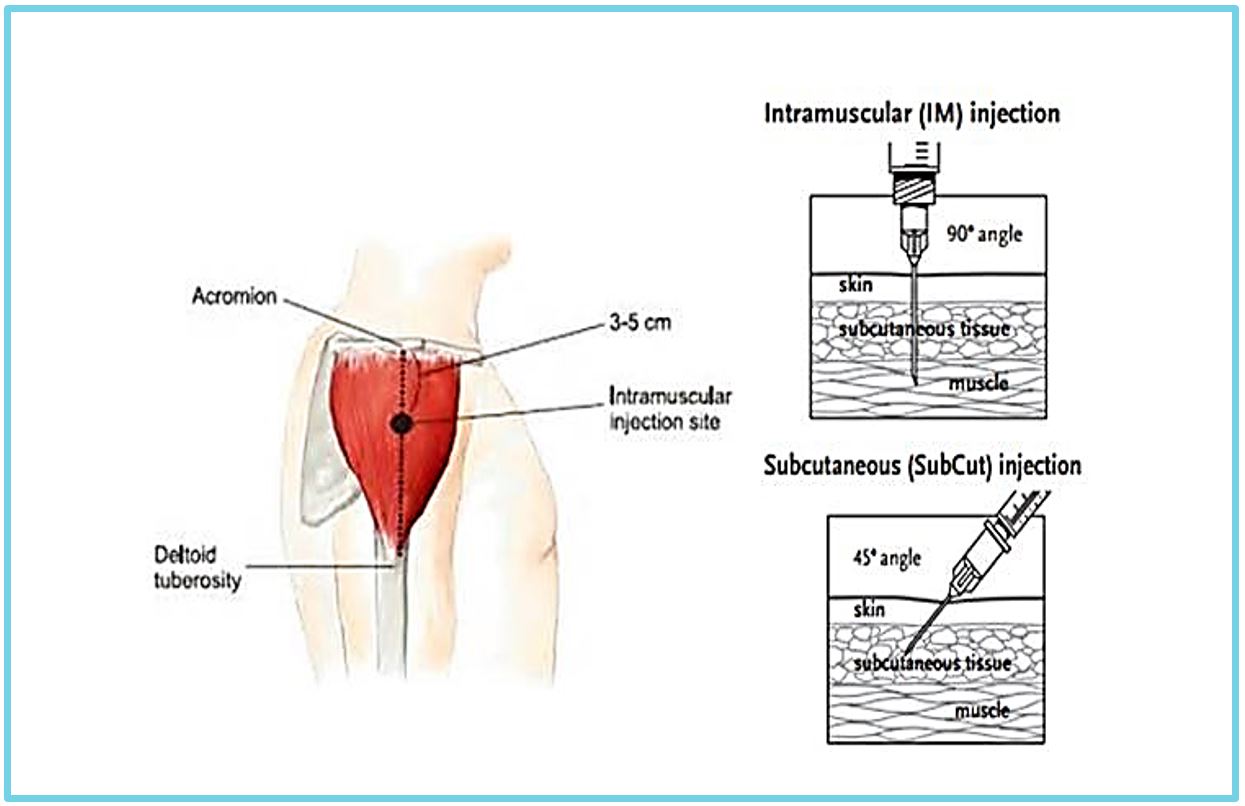 an intramuscular (IM) technique, with the needle piercing the skin at a 90° angle with the skin stretched out at the site of injection. IM is the preferred route for the flu vaccination, even for customers who are on anticoagulation therapy or have bleeding disorders. On the next page, you can watch a video by ECG on delivering intramuscular injections.
an intramuscular (IM) technique, with the needle piercing the skin at a 90° angle with the skin stretched out at the site of injection. IM is the preferred route for the flu vaccination, even for customers who are on anticoagulation therapy or have bleeding disorders. On the next page, you can watch a video by ECG on delivering intramuscular injections.
Subcutaneous injections are delivered in to the arm with the needle at a 45° angle to the skin, and the skin should be pinched at the site of administration before delivering the injection. On the next page, you can watch a video by ECG on delivering subcutaneous injections.
Always check the PGD and the vaccine's licence for each product to check the recommended route of administration as they may vary.
If an individual is receiving two or more injections in the same visit, they should be given in separate sites and preferably in different limbs. If they’re given in the same limb, they should be administered at least 2.5cm apart. The site of all injections should be recorded in the individual’s records.
Some individuals may be nervous about receiving an injection. If so, it is a good tip to try:
- Distracting the individual, by talking to them.
- Position a poster or picture on the wall for them to look at.
- Maintain a calm demeanour to put them at ease and provide reassurance.
- Prepare the injection out of sight.
