What is an allergy?
An allergy is an unnecessary immune response to a normally harmless substance. Allergies are very common. According to NHS Scotland they're thought to affect more than 1 in 4 people in the UK at some point in their lives.
Allergic reactions begin in your immune system. When a typically harmless substance is encountered by a person who is allergic to it, the immune system may overreact by producing antibodies that "attack" the allergen. This can cause wheezing, itching, runny nose, watery or itchy eyes, and other symptoms.
Allergies can range in severity from symptoms of mild discomfort to the life-threatening systemic reaction seen in anaphylaxis.
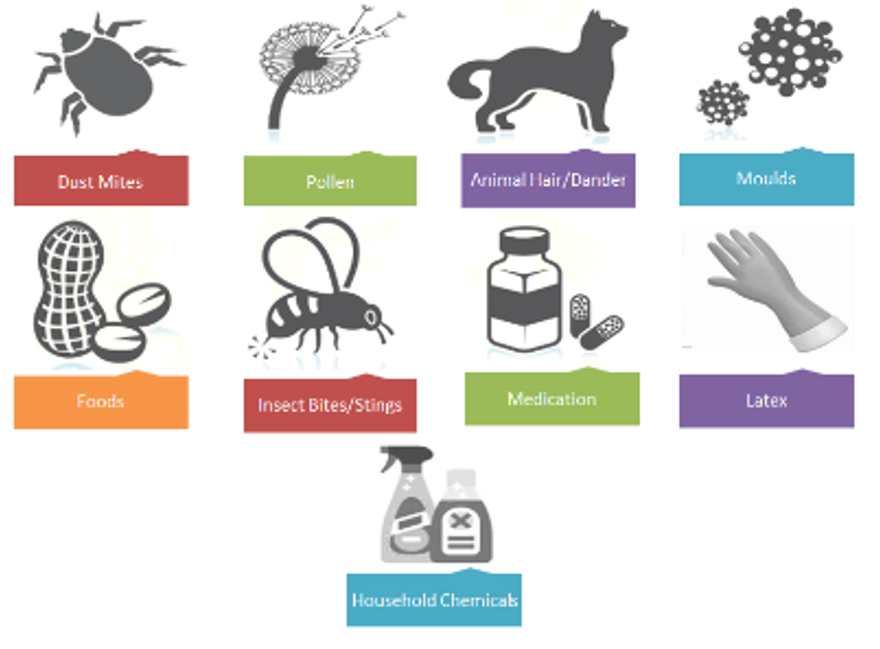
Examples of common substances people are allergic to include pollens, dust mites, insect venom and foods such as nuts or shellfish. When these substances cause an allergic reaction they are considered an allergen.
Allergic reactions can be grouped into two classes:
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) mediated
- Non-IgE mediated
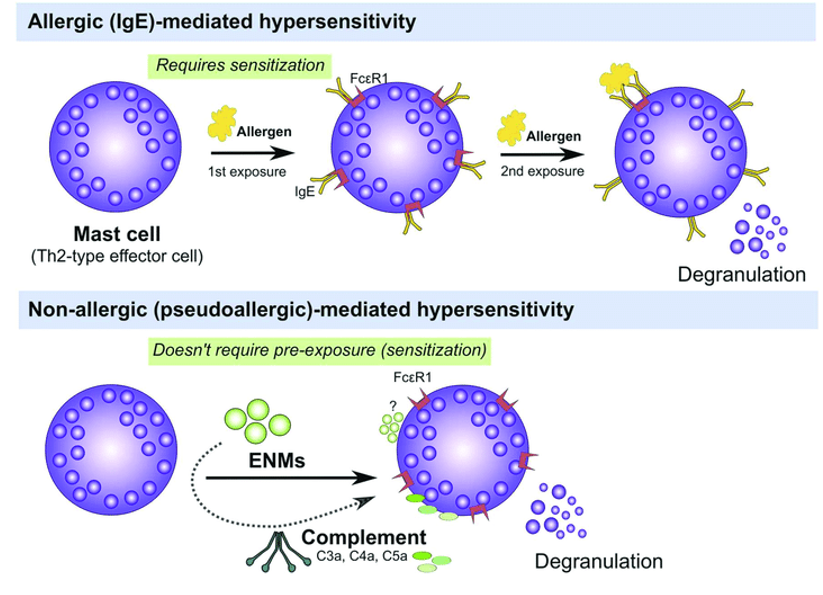
IgE mediated – most common.
IgE is a type of antibody produced by the immune system.
If you have an allergy, your immune system overreacts to an allergen by producing IgE. These antibodies travel to cells that release chemicals, causing an allergic reaction. This reaction usually causes symptoms in the nose, lungs, throat, or on the skin.
Each type of IgE has specific "radar" for each type of allergen. That's why some people are only allergic to cat dander (they only have the IgE antibodies specific to cat dander); while others have allergic reactions to multiple allergens because they have many more types of IgE antibodies.
Non-IgE mediated - According to the website Children's Allergy Doctors these are often delayed food allergies which are caused by a reaction involving other components of the immune system apart from IgE antibodies. The reactions do not appear immediately, often taking longer to develop (hours to days). Symptoms can include one or more of the following:
- Dry, itchy and red skin (eczema).
- Abdominal discomfort or colic during infancy.
- Reflux (vomiting) or silent reflux (pain).
- Diarrhoea, mucous or blood in stools.
- Poor weight gain.
- More rarely, constipation.
Although they can happen any time in a person’s life they are most commonly seen in infants in the first few months of life.