The main aim of treatment of stable angina is to relieve symptoms and prevent angina attacks by improving myocardial oxygen supply or reducing cardiac workload and hence myocardial oxygen demand. Effective treatment will minimise symptoms, improve quality of life, long term morbidity and mortality.
Management options include lifestyle changes, drug treatment and revascularisation.
NICE guidelines specify that optimal treatment for stable angina involves one or two anti-anginal drugs combined with drugs for the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease.2
Diagrammatic representation of NICE guidelines for the treatment of angina:
Please refer to this chart when reading the following sections.
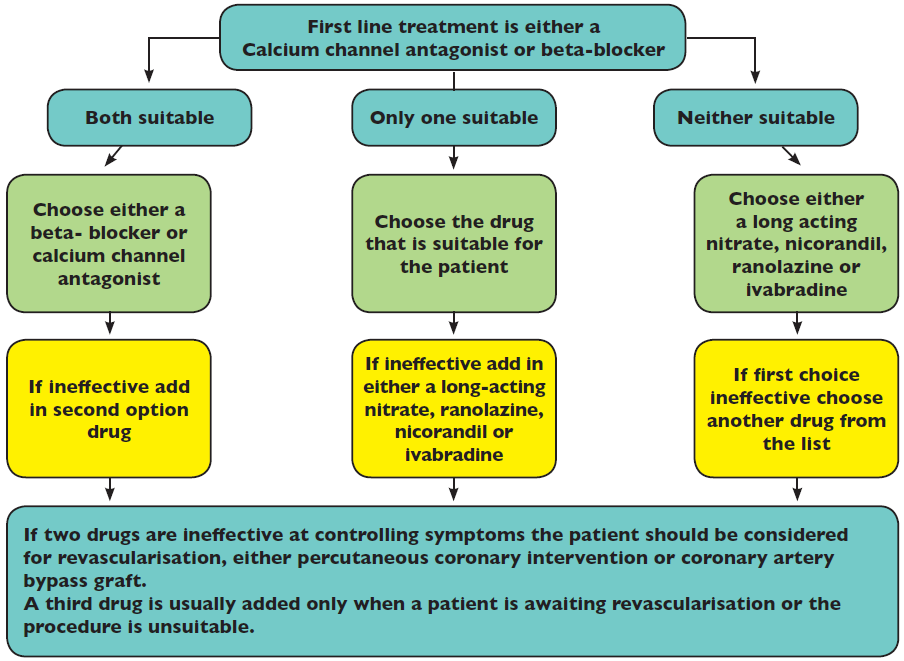
NICE guidelines differentiate treatment of patients with stable angina into three distinct areas:
- Relief of symptoms
- Prevention of episodes of angina
- Secondary prevention of cardiovascular events
