Calcium channel blockers interfere with the inward movement of calcium ions through the slow channels of active cell membranes. This affects myocardial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, cells involved in the conduction of electrical impulses and also gastrointestinal smooth muscle.
The blockade of inward movement of calcium ions can result in a reduction of myocardial contractility, vascular or coronary muscle tone and the formation or propagation of myocardial impulses.
This action results in calcium channel blockers having three key clinical effects:
- Reduction in the force and rate of myocardial contraction
- Coronary vasodilation
- Peripheral vasodilation
Blockade of the calcium channels in the gastro-intestinal mucosa results in constipation. This is a recognised side effect of verapamil.
Calcium channel blockers can either be dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine, nifedipine or felodipine or the non-dihydropyridine 'rate limiting' calcium channel blockers such as diltiazem or verapamil.
The different categories of calcium channel blockers have distinct actions that influence their clinical use, as shown in the table below6:
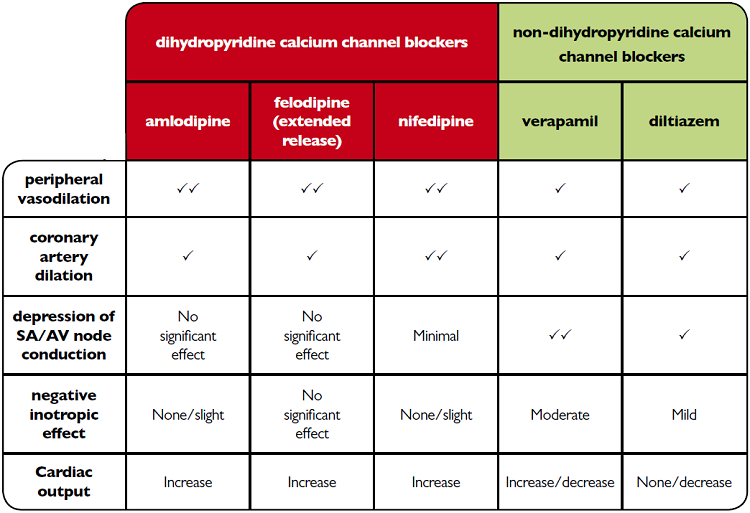
The dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers have a more selective action at the vascular sites than the myocardial sites, resulting in a greater vasodilator effect.
Verapamil has a predominantly myocardial action which reduces the rate and force of myocardial contraction, whilst diltiazem has an intermediate effect on the vascular and myocardial sites.
Calcium channel blockers can be used as monotherapy for angina or in combination with other anti-anginal agents. The rate controlling effect of verapamil and diltiazem may be beneficial for patients who are unable to take beta blockers.
Patients should be advised to not suddenly stop taking their calcium channel blocker, unless advised by the prescriber, as this can exacerbate angina symptoms.
Side effects associated with calcium channel blockers can include constipation and bradycardia (especially for diltiazem and verapamil), whilst vasodilation results in headaches, ankle swelling, flushing and postural hypotension.
