The Equality Act 2010 stipulates nine "protected characteristics" in which people can be protected from discrimination.
We all have some protected characteristic and anyone can be protected if they feel they have been discriminated against due to the characteristics.
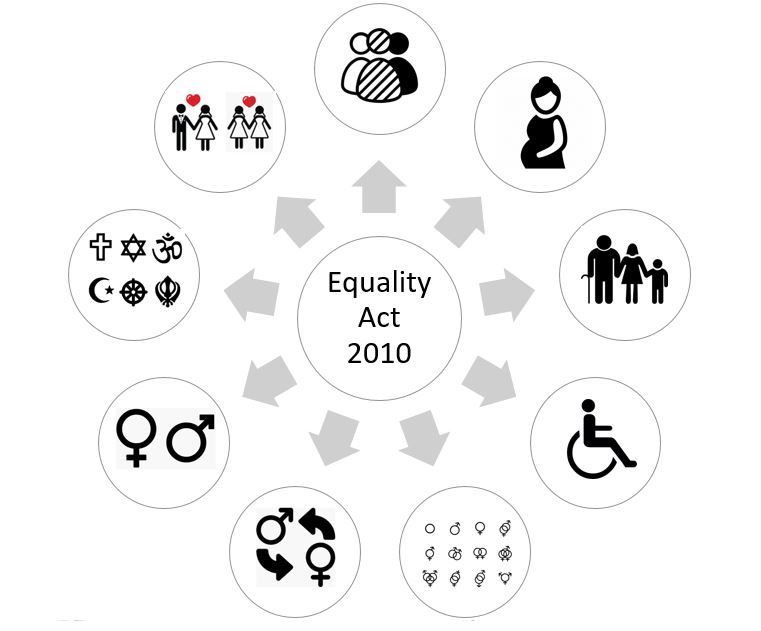
Age - The act protects people of all ages. The act removed the default retirement ago so most jobs have no upper age limit or set retirement age. Employers can insist on being a certain age however, for example they may need to be able to drive, or serve alcohol
Disability - The act defines a disabled person as one who has a physical or mental impairment which has a substantial and long term adverse effect on their ability to carry out normal day to day activities. The act prevents employers from asking questions about an applicants health, absences from work or disability before making an offer of employment.
Gender Reassignment - The act provides protection for a trans person; someone who proposes to, starts or has completed a process to change gender. An individual doesn't have to be under medical supervision to be protected by the act.
Marriage and Civil Partnership - The act protects employee who are married or in a civil partnership against discrimination because of their marital status. The act does not cover single people or couples in a relationship which is not recognised.
Pregnancy and Maternity - A woman is protected against discrimination on the grounds of pregnancy and maternity during the period of her pregnancy and any statutory maternity leave she is entitled to.
Race - It is unlawful to discriminate against people at work because of their race. For the purposes of the Equality Act 2010 race includes colour, nationality, ethnic or national origins. A racial group can be made up of two or more different racial groups.
Religion or Belief - Under the Equality Act 2010 religion can include any religion which has a clear structure and belief system. Belief means any religious or philosophical belief someone might hold. People are also protected if they don't have a particular religion or belief. Discrimination can occur even when both the discriminator and the person being discriminated against have the same religion or belief.
Sex - Sex refers to the gender of an employee so both men and women are protected under the act. It is unlawful to discriminate against people at work because of their sex (gender)
Sexual Orientation - The act protects bisexual, gay, heterosexual and lesbian people from discrimination or harassment.
There are occupation requirements which may allow some discriminatory acts to be justified in certain circumstances. For example, the Roman Catholic church does not allow female priests, so an exemption can apply in this case.
