The sun is an important part of our general health and well being; it can have an influence on our mood and help us generate vitamin D which helps to keep bones and teeth healthy. However the sun can cause damage to the skin which can range from short-term effects such as sunburn right through to long-term damage which could result in skin cancer.
When skin is exposed to sunlight a coloured pigment called melanin is produced. This stops the skin from burning easily but it does not prevent the harmful effects of the UV rays. It is the melanin that causes the skin to go darker and a suntan to develop.
Exposure to high levels of UVA and UVB increases the risk of developing skin cancer therefore it is very important to protect the skin. The best ways of protecting the skin are sun avoidance, covering up and sun screens.
Below are some top tips to advise customers:-
- Avoid the Sun - when it is at its strongest by staying indoors or using shade. In the UK the sun is at its strongest during the middle of the day between 11am and 3pm
- Cover Up - When out in the sun use a wide brimmed hat to protect the face and neck as these are more commonly affected by sun damage. It is important that children wear a hat with a neck protector as they are more vulnerable to skin damage
- Wear wraparound sunglasses - To protect the eyes from sun damage sunglasses should conform to European standard and display the CE mark which show they protect against UV light.
- Use a high factor sun protection - A sun cream should have a sun protection factor of at least 15 or above, depending on your skin type and holiday destination.
Sun Protection factor, commonly known as SPF, is the guide used to show how much sun protection a particular sunscreen provides. SPF protects against the damaging UVB rays which cause sunburn and can cause skin cancer. It is important that the sun protection product also provides protection against UVA rays. UVA protection is shown by a start system ranging from 0-5.
SPF indicates how long someone wearing protection can stay in the sun without bruning compared to not wearing SPF.A person whose unprotected skin would begin to burn after 15 minutes could extend their exposure to the sun to five hours if they correctly applied and re-applied SPF20. To work this out you multiply the burn time by the SPF, so 15 minutes x (SPF) 20 = 300 minutes or five hours.
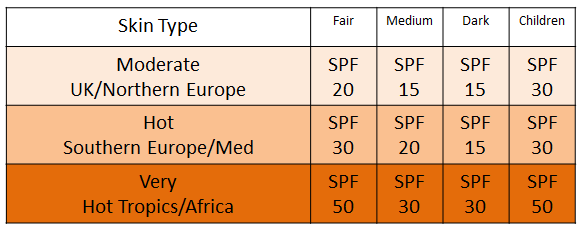
SPF ranges from 2 to 50. For an adult the minimum recommended SPG is 15 whilst children and adults with pale skin an SPF of 30 should be recommended.
The table below offers a guide to the different SPF , however it is important to use the information as a reference point as it will depend on their skin type and destination.